Geopolitical Background
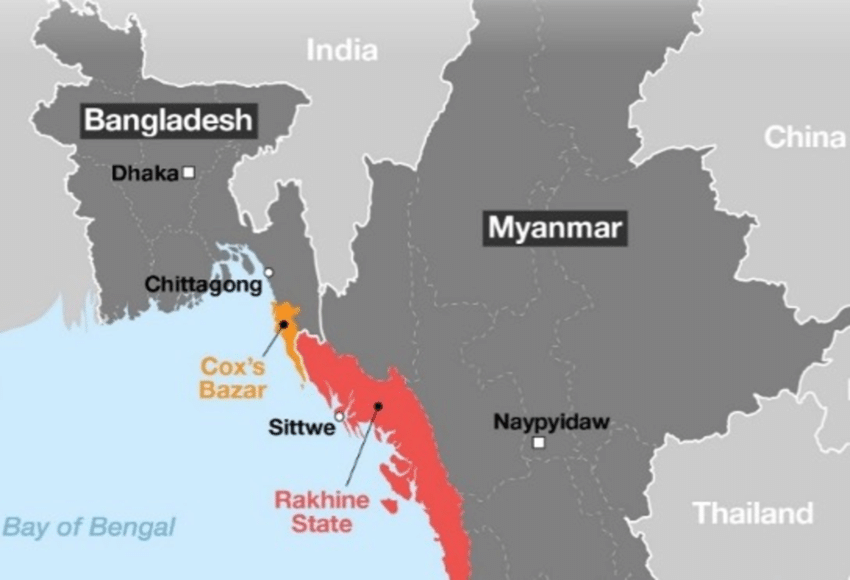
The Bangladesh-Myanmar border stretches approximately 271 kilometers, characterized by the Naf River, hilly terrain, and dense forests. On Myanmar’s side lies the Rakhine State, while Bangladesh’s side includes the Chittagong Hill Tracts and Teknaf Peninsula. This region has been a hotspot for geopolitical and humanitarian crises, notably the mass migration of Rohingya Muslims in 2017.
Key Geographical Features:
- Naf River: Flows from north to south, merging into the Bay of Bengal.
- Teknaf Peninsula: A vital area for refugee crossings.
- St. Martin’s Island: A small island off the Teknaf Peninsula, now under contested control.
Key Actors in the Conflict
1. Arakan Army (AA):
- Ethnic Base: Predominantly Buddhist.
- Goals: Autonomy for the Rakhine people.
- Capabilities: Larger, organized, and militarily equipped, controlling strategic locations, including sections of the Bangladesh-Myanmar border.
- Conflict Involvement: Direct clashes with Myanmar’s military (Tatmadaw) and the Arakan Rohingya Salvation Army (ARSA).
2. Arakan Rohingya Salvation Army (ARSA):
- Ethnic Base: Rohingya Muslims.
- Goals: Rights and autonomy for the Rohingya.
- Capabilities: Smaller, operating primarily as an insurgent group.
- Tactics: Hit-and-run strategies, ambushes, and raids.
Both groups are adversaries due to deep ethnic and political differences but share a common enmity toward Myanmar’s military. Despite this, their operations have increasingly destabilized the region.
Broader Geopolitical Implications
Myanmar’s Internal Dynamics
Myanmar is a Buddhist-majority nation, where Buddhist groups often perceive the growing Muslim Rohingya population as a cultural and demographic threat. This perception has fueled ethnic conflicts and heightened tensions along its borders.
The Role of External Forces
The involvement of powerful global players, referred to as “2119” in some narratives, has exacerbated the conflict:
- Natural Gas Reserves: The Bay of Bengal’s delta region contains significant natural gas deposits, a key point of contention.
- Strategic Interests: Control of St. Martin’s Island and the Teknaf Peninsula is pivotal for influence over the Indo-Pacific region.
Bangladesh’s Political Landscape
- Rohingya Refugee Crisis: Over a million refugees reside in Cox’s Bazar, with recent unrest forcing further displacement into Indonesia, Malaysia, and deeper into Bangladesh.
- August 2024 Coup: Sheikh Hasina’s government was overthrown, allegedly orchestrated by external forces aiming to realign Bangladesh’s geopolitical stance.
- Interim Government: Muhammad Yunus, a Nobel laureate, is at the helm, raising questions about his ties to Western interests.
The 2119 Connection
Origins of Arakan Army and ARSA:
- Formation Dates: The Arakan Army emerged in 2009, and ARSA in 2013—closely aligning with key geopolitical shifts in the region.
- Deep State Influence: Allegations suggest that both groups were created and supported by external forces, including 2119 and China, to exploit regional instability.
Strategic Goals:
- Establishing military bases in the Teknaf Peninsula and St. Martin’s Island to influence the Indo-Pacific region.
- Controlling natural gas reserves and securing strategic trade routes.
The Impact on Bangladesh
Refugee Crisis Escalation
The ongoing conflict has rendered large areas of the Teknaf Peninsula uninhabitable. Rohingya refugees, already living in precarious conditions, face further displacement, exacerbating regional instability.
Military and Governance Challenges
- Territorial Losses: Bangladesh has lost control over significant areas, including St. Martin’s Island.
- Foreign Influence: Allegations of external orchestration in the recent coup point to broader geopolitical games being played at Bangladesh’s expense.
India’s Role
India has engaged with the Arakan Army for strategic infrastructure projects, signaling a nuanced approach to the region’s complex dynamics. While India’s Ministry of External Affairs has discreetly hosted discussions with various resistance groups, its direct involvement remains ambiguous.
The Bigger Picture
The Bangladesh-Myanmar border crisis is a microcosm of larger geopolitical struggles. Natural resources, ethnic conflicts, and external interventions have created a volatile mix, with regional and global implications. The involvement of major powers and the destabilization of Bangladesh highlight the intricate web of interests and conflicts in the region.
Conclusion
Addressing the Bangladesh-Myanmar border issue requires a multifaceted approach involving regional cooperation, humanitarian aid, and international oversight. The stakes are high, not just for Bangladesh and Myanmar but for the entire Indo-Pacific region. Understanding the historical, political, and economic dimensions of this crisis is crucial for formulating effective solutions.
Also Read: Attack on Germany Shocks the World: Geopolitical Implications
Disclaimer: This blog post is based on publicly available information and does not reflect any political bias or endorsement. Readers are encouraged to explore diverse sources for a comprehensive understanding of global events.
Follow US